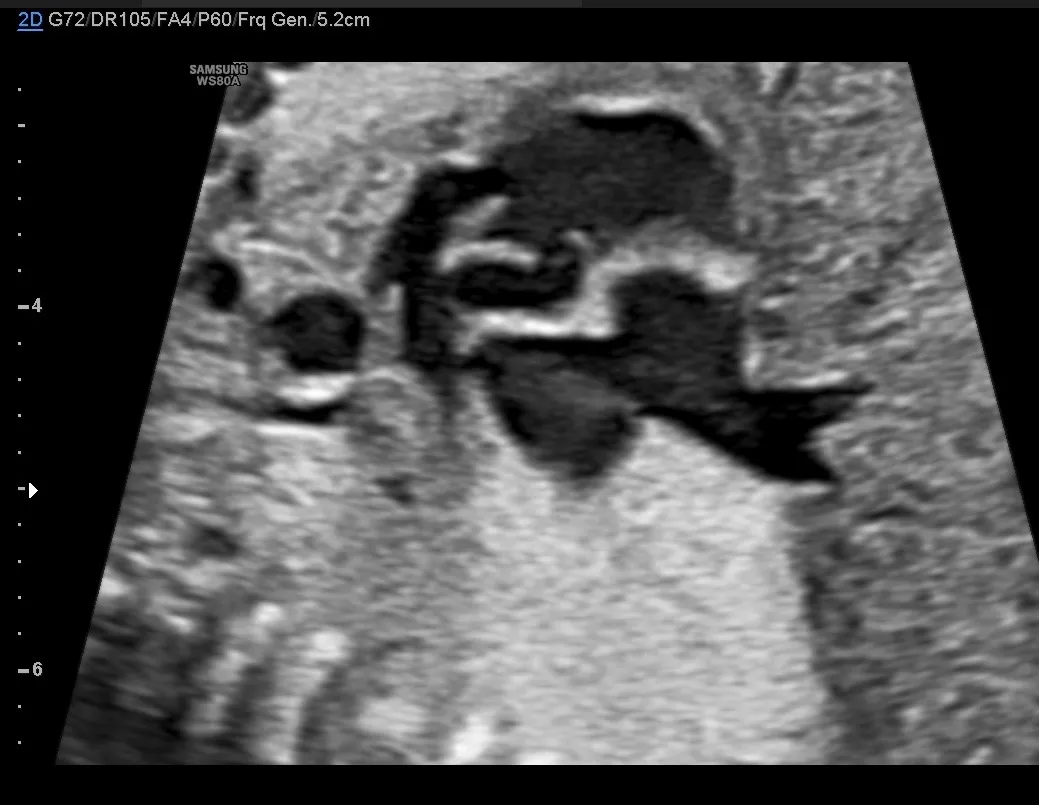
It's classical case of Tetralogy of Fallot.
DESCRIPTION
Prenatally only three features of TOF are seen:
-
perimembranous VSD,
-
anterior deviation of the aorta and
-
small pulmonary artery.
The fourth feature of TOF, right ventricular hypertrophy, is seen only postnatally.
The four-chamber view is usually normal, as the VSD is located in the memebranous part of the septum, except when TOF is associated with AVSD.
The cardiac axis is often displaced leftwards
- The first great artery (aorta) arises from the centre of the heart and sits astride the crest of the ventricular septum (overriding aorta) above the VSD.
- The great arteries are normally related but the pulmonary artery is smaller than the usually enlarged aorta.
Prognosis
Classic TOF (with pulmonary stenosis) usually requires one operation (mortality < 5%) during the first year of life with a good long-term outcome.
However, in complex cases of TOF (with pulmonary atresia or absent pulmonary valve syndrome) more than one intervention is usually necessary with less favourable outcome.